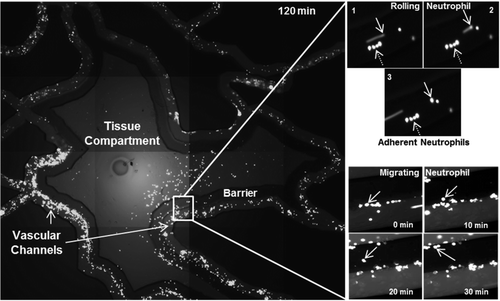
Bioinspired Microfluidic Assay for In Vitro Modeling of Leukocyte–Endothelium Interactions
Authors: G. Lamberti, B. Prabhakarpandian, C. Garson, A. Smith, K. Pant, B. Wang, and M.F. Kiani. Anal.
Chem., 2014, 86 (16), pp 8344–8351 DOI:10.1021/ac5018716
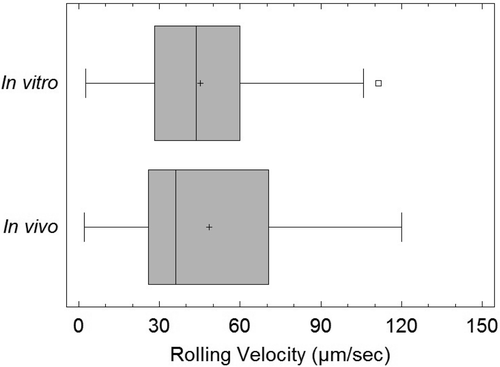
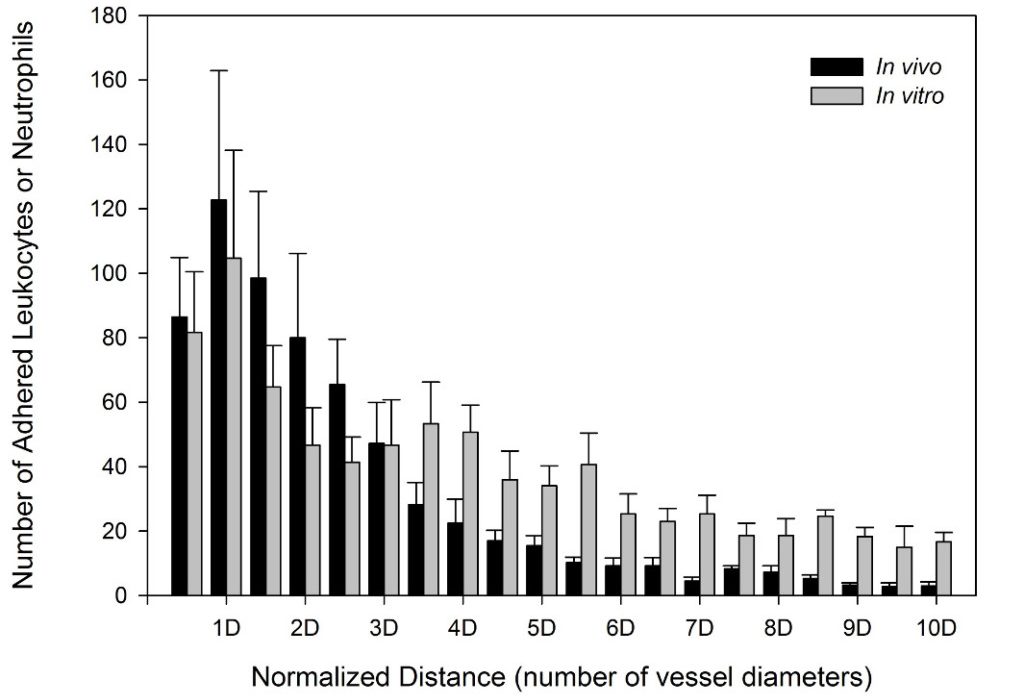
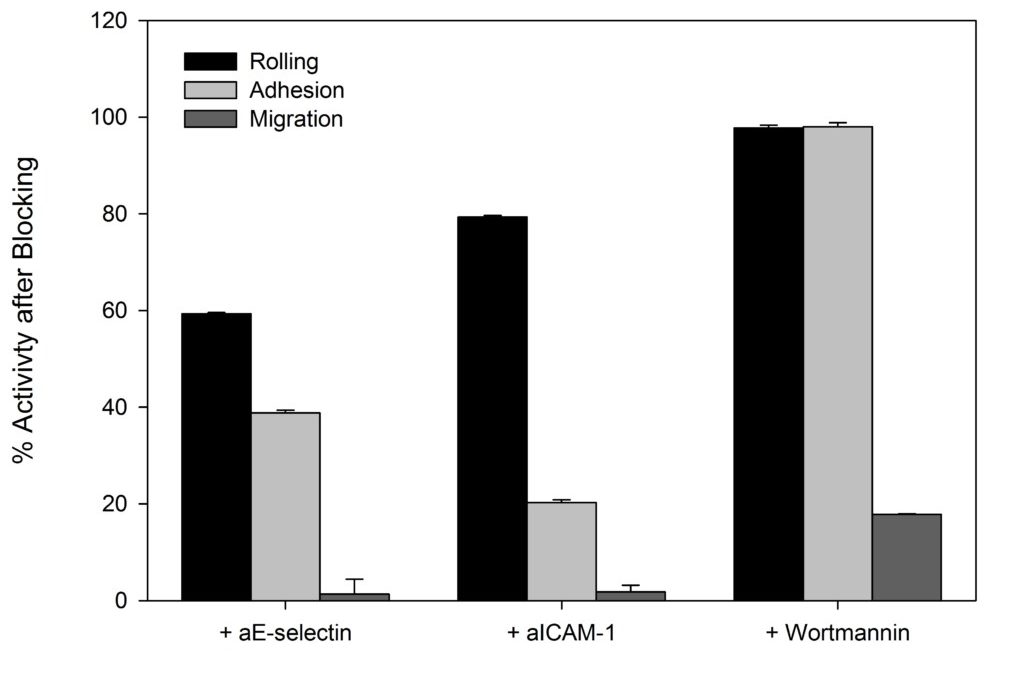
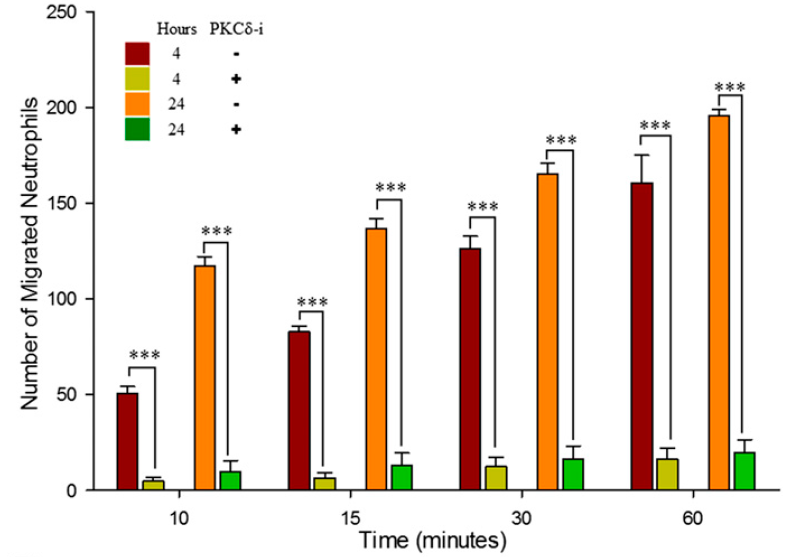
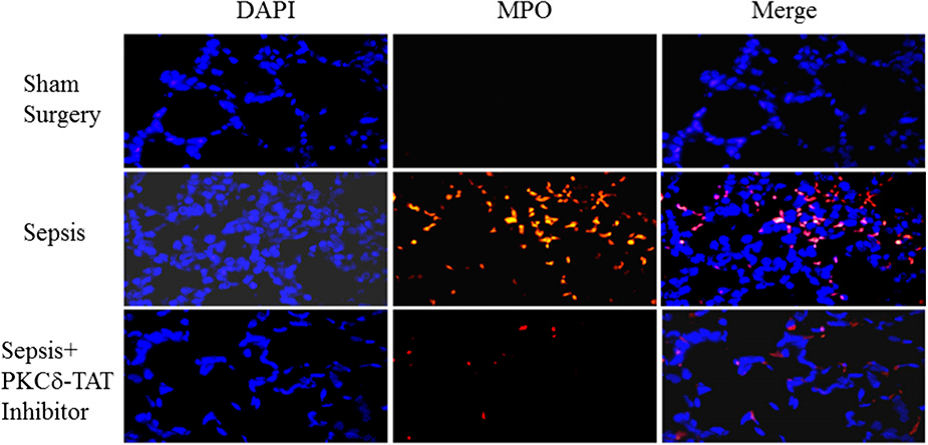
SynRAM microfluidic chips comprising of realistic microvascular networks were used to understand the role of classical inhibitors of individual steps of the leukocyte adhesion cascade. Experimental results matched very well with in vivo data highlighting the unique ability of the platform for real-time analysis of these dynamic events in a morphologically realistic environment (Lamberti et al 2014).